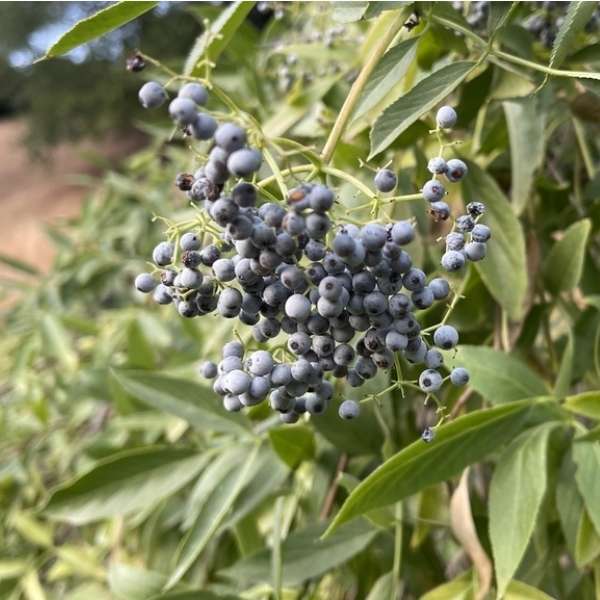
Blue Elderberry, Mexican Elderberry, or Tapiro is a deciduous shrub or small tree, growing up to as tall as 30 feet. It is native from Oregon to Baja all the way to western Texas. It has cream or yellow flowers in the spring and purple berries in the fall. Its berries are one of the most important source of food for birds in California. Blue Elderberry is tough, easy to grow, and grows very rapidly. It can grow from a 1 gallon container to a 15 foot tree in 3 years if happy. It handles a variety of different soil moisture levels once established. It can handle permanently moist soil near stream sides or seeps, and will thrive next to or in regularly irrigated areas. Once established, it also grows well in fairly dry soils, though in drier conditions it will normally go deciduous or semi-deciduous in the summer and fall, and green up in the early winter. Drought-stressed Blue Elderberry’s often end up more attractive than ones that get plenty of year round water, frequently developing interesting gnarled branches and thicker though shorter trunks over time. It likes part shade or sun, and will tolerate full shade, though in full shade it will look rangy as its branches search out for more sun. Description from calscape.org
Home > Plant Guide >
Scientific Name
Family
Garden Type
Wildlife
Native Plant Region
Light needs
Water Needs
Plant Type
Bloom Color(s)
Height
Width
Months in Bloom
Safe Beneath Power Lines?

We’d like to maintain accurate and robust plant listings. If you see information that is not correct or that could be added to improve the listing, please let us know. Or if you’d like to suggest a plant to add to our plant guide, you can use this form do so. Thank you!

Learn about container gardening with shrubs, trees, herbs, veggies, perennials, and annuals. A special focus will be on plantings that provide pollinators with food and that encourage bird habitat.

Learn about diversifying the way architecture is taught and practiced from designers of color.
Get involved by sharing and mapping the birds, animals and nature around you to help the community understand the biodiversity in our neighborhood.

Look closer…and meet the local insects that pollinate the plants around your Seattle neighborhoods. Learn about some of our amazing native pollinating insects.

New types of vegetation can attract additional wildlife to an area. You might be surprised how a little green can go a long way!

Check out our list of local wildlife-supporting plant stores and nurseries, organizations, and community science opportunities.
Nature of Your Neighborhood is a collaboration between Birds Connect Seattle, the Capitol Hill EcoDistrict, and the Seattle Bird Conservation Partnership. Our goal is to foster relationships between the people and the nature of their neighborhoods.